NASA Tests More Printed Rocket Engine Parts

Latest News
November 21, 2014
NASA continues to move toward 3D-printed rocket engine components. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne have conducted 19 hot-fire tests on four injector and thrust chamber assembly configurations using copper alloy materials at the Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The tests are part of NASA’s Game Changing Development Program in the Space Technology and Mission Directorate.
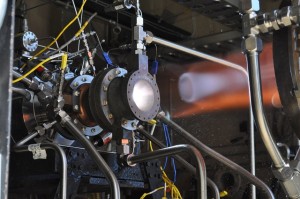 According to NASA, this is the first time that tests confirmed 3D-manufactured copper parts could withstand the heat and pressure required for space launches.
According to NASA, this is the first time that tests confirmed 3D-manufactured copper parts could withstand the heat and pressure required for space launches.
“The successful hot fire test of subscale engine components provides confidence in the additive manufacturing process and paves the way for full scale development,” said Tyler Hickman, lead engineer for the test at Glenn.
In August, NASA tested 3D-printed injectors at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The rocket engines in those tests included what NASA says are the most complex 3D-printed components it has tested to date. The rockets include printed injectors, and each of them burned for five seconds, producing 20,000 lbs. of thrust.
According to NASA, the printed injectors can provide more precise alignment and lower production costs. The printed injectors consist of just two parts, compared to the 160 components required for traditionally manufactured injectors.
Solid Concepts and Directed Manufacturing each built one of the injectors. The injector from Directed Manufacturing was built using selective laser melting.
Those injectors were modeled after ones used in large engines such as the RS-25 engine that will power the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will be used to launch missions beyond Earth’s orbit.
“One of our goals is to collaborate with a variety of companies and establish standards for this new manufacturing process,” said Marshall propulsion engineer Jason Turpin. “We are working with industry to learn how to take advantage of additive manufacturing in every stage of space hardware construction from design to operations in space. We are applying everything we learn about making rocket engine components to the Space Launch System and other space hardware.”
You can see a video of the injector tests below.
Source: NASA
Subscribe to our FREE magazine, FREE email newsletters or both!
Latest News
About the Author
Brian Albright is the editorial director of Digital Engineering. Contact him at [email protected].
Follow DE