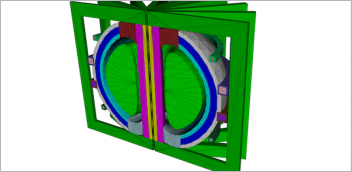
WoeLab Build 3D Printer from E-Waste

Image courtesy of Woelab.
Latest News
January 3, 2018
E-waste is a growing problem in Africa, where certain countries have become dumping grounds for cast-off electronics from Europe and North America, and others struggle to manage their own waste flows. In places like Ghana, e-waste is often burned in massive dumps along with other garbage, creating toxic fumes.
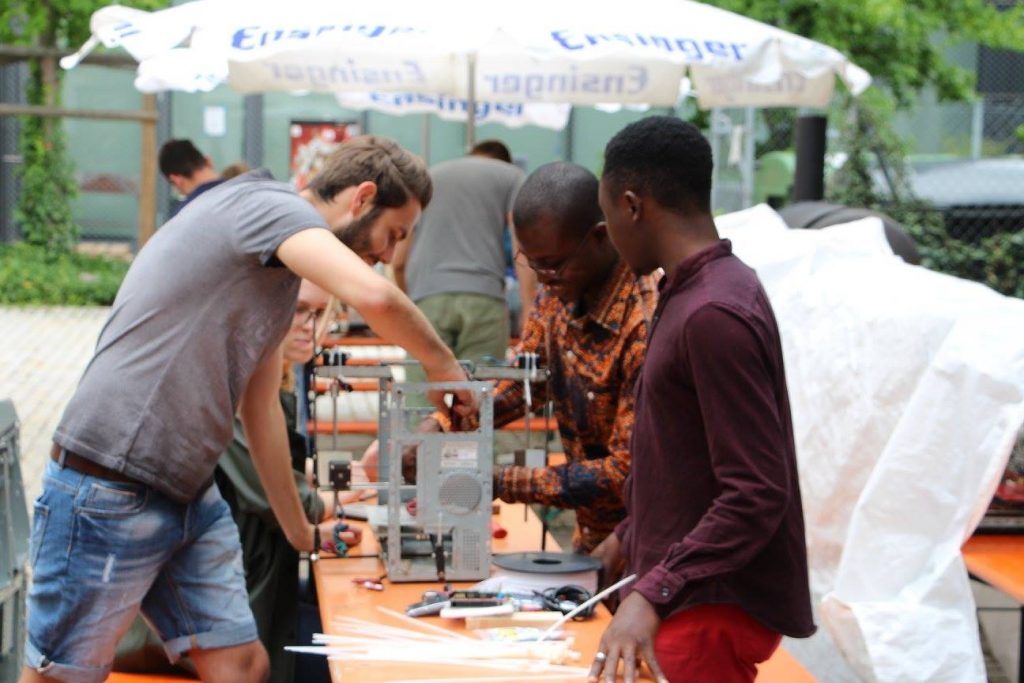 Image courtesy of Woelab.
Image courtesy of Woelab.Recycling efforts are increasing on the continent, and one laboratory in Lomé, the capital of the West African nation of Togo, has created a 3D printer built from e-waste.
WoeLab is a community technology hub and network of local inventors and entrepreneurs. Staff there built the 3D printer using parts from old printers, computers and scanners. Founder and architect Sénamé Koffi Agbodjinou was inspired to build the printer after purchasing an off-the-shelf model for the lab.
The printer is based on the RepRap 3D printer from the University of Bath.
The first model was finished in 2013, and they have since built 20 more. The group hopes to place a 3D printer at every school within 1Km of the lab.
“What we are concerned with is to try to create in the young people a confidence in themselves in their capacity to realize projects,” Agbodjinou told CNN.
Other organizations have also turned to e-waste to enable 3D printing. Students at the Buni Hub mini-fabrication lab in Tanzania also built a printer from e-waste. (The students also reverse-engineered a drone using scrap parts.)
Agbodjinou and his counterparts hope to increase recycling of electronic waste (less than one-sixth is currently recycled or reused) while also creating new ways for residents to generate income and improve technology access.
Grassroots programs like this will have their work cut out for them. Global e-waste is expected to reach 49.8 million tons in 2018.
There are other signs of improvement on the continent. South Africa, for instance, has enforced e-waste handling regulations. The East Africa Communications Organization is working to harmonize e-waste policies for its six member countries, and Rwanda has launched an e-waste recycling initiatives that includes the opening of an advanced recycling facility in Bugesera.
Source: CNN
Subscribe to our FREE magazine, FREE email newsletters or both!
Latest News
About the Author
Brian Albright is the editorial director of Digital Engineering. Contact him at [email protected].
Follow DE